19 November 2009 | Integral Network Solutions
Networks benefit from Structured Cabling developments
Over the years voice and data cabling requirements have merged. Today, cabling infrastructures are designed to support voice, data, video and other communications services such as video conferencing, cable TV and security applications such as CCTV.
The preferred cabling media in the UK is either unshielded or shielded balanced twisted pair cables which have progressed to a stage in development where a bandwidth of over 200MHz is now available. Each communications cable provides four twisted pairs between two points in a network.Structured cabling is a buildings'' telecommunications cabling infrastructure. This infrastructure as a whole consists of a number of smaller elements known as subsystems.
These subsystems include (but are not limited to):
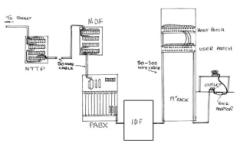
• Backbone cabling which connects between the entrance facilities, equipment rooms and telecommunications rooms.
• Horizontal cabling which connects telecommunications rooms to specific outlets on the floor.
• Telecommunications rooms which house the equipment connecting the backbone and horizontal cabling.
The design and installation of structured cabling is governed by a set of standards for data or voice communications, using category 5 or category 6 cable and modular sockets. (Cables can also be known as Cat 5e or Cat 6). These standards outline how to lay the cabling in a “star formation”. This means that all outlets are terminated at a central patch panel (normally 19 inch rack-mounted inside the communications cabinet in the telecommunications room − also sometimes known as a server room). From this patch panel it can be decided how these connections will be used.
Each outlet can be ''patched'' into a data network switch, or into a ''telecoms patch panel'' which forms a bridge into a private branch exchange (PBX) telephone system - this makes the connection a voice port rather than a data port. It is common practice to color code patch panel cables to identify the type of connection, though structured cabling standards do not require it.
Current data cabling standards specify that all eight connectors in Cat5, Cat 5e and Cat 6 cable are connected, this means that you cannot ''double-up'' or use one cable for both voice and data. Structured cabling schemes provide connections from individual points around a building to a central patching location within a communications cabinet.
Voice switch, LAN hub and telecommunications services are presented at the patch panel and peripherals can be cross-connected to deliver the necessary service wherever they are needed around the building.Structured Cabling is the glue that connects everything − from network services, such as ISDN, ADSL, WAN, and LAN to multimedia, voice and data.
Your cabling infrastructure can be configured and adapted to meet new demands, and can accommodate any moves staff need to make, either individually or collectively, on a temporary or permanent basis. Additions, moves and changes to your structured cabling can be made easily.